Office-Based Breast Biopsy:
What is cryoablation?
Cryoablation refers to procedures that use extremely cold temperatures to destroy diseased tissue, including cancer cells. Liquid nitrogen or argon gas is the freezing agent. The Visica 2 Treatment System uses liquid nitrogen. Cryoablation was initially used to ablate skin lesions, but its applications have expanded to treat cancers of the prostate, liver, lung and kidney, as well as certain cancers that have metastasized. It is also referred to as percutaneous cryoablation or cryotherapy.
Is cryoablation a new technology?
No. Cryoablation has been used in open or laparoscopic surgical procedures for over 50 years. Today, cryoablation is routinely done percutaneously (through the skin) with small incisions and under image-guidance i.e., ultrasound, CT or MRI. Cryoablation causes tissue necrosis by freezing the targeted tissue and damaging the microvasculature structure that feeds the cells.
How is cryoablation performed?
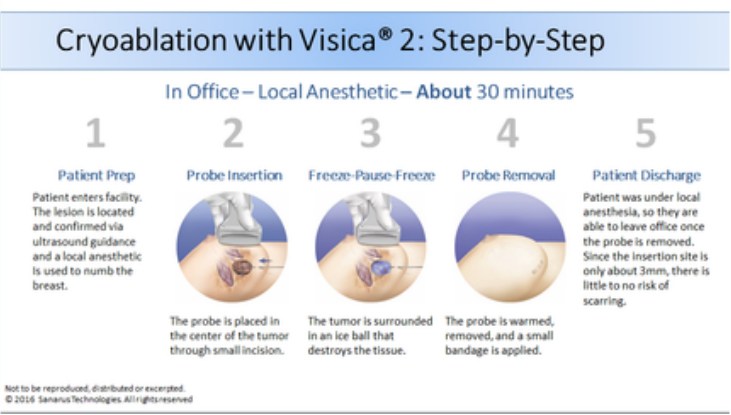
The breast is numbed with local anesthesia. The physician inserts a hollow-tipped probe through a small incision and inserts it into the tumor under ultrasound guidance. Closed-loop liquid nitrogen passes through the probe and forms an ice ball around the lesion. Damage to healthy surrounding tissue is minimal. Freezing destroys the tumor cells, which are then gradually reabsorbed and expelled by the body over 3-18 months.
How long does the procedure take?
The procedure is performed in our office and takes less than 30 minutes. Most patients report minimal discomfort and are able to resume normal activity right away. Since no breast tissue is removed, the shape of the breast is maintained and little, if any, visible scarring occurs.
Who is a good candidate for cryoablation?
Cryoablation is a safe and effective option for patients whose breast tumor is less than 4 cm in diameter, visible on sonogram and has been confirmed with a biopsy.
Pictured below you will find a step-by-step example of the process of Cryoablation along with an animation of the procedure
Cryoablation refers to procedures that use extremely cold temperatures to destroy diseased tissue, including cancer cells. Liquid nitrogen or argon gas is the freezing agent. The Visica 2 Treatment System uses liquid nitrogen. Cryoablation was initially used to ablate skin lesions, but its applications have expanded to treat cancers of the prostate, liver, lung and kidney, as well as certain cancers that have metastasized. It is also referred to as percutaneous cryoablation or cryotherapy.
Is cryoablation a new technology?
No. Cryoablation has been used in open or laparoscopic surgical procedures for over 50 years. Today, cryoablation is routinely done percutaneously (through the skin) with small incisions and under image-guidance i.e., ultrasound, CT or MRI. Cryoablation causes tissue necrosis by freezing the targeted tissue and damaging the microvasculature structure that feeds the cells.
How is cryoablation performed?
The breast is numbed with local anesthesia. The physician inserts a hollow-tipped probe through a small incision and inserts it into the tumor under ultrasound guidance. Closed-loop liquid nitrogen passes through the probe and forms an ice ball around the lesion. Damage to healthy surrounding tissue is minimal. Freezing destroys the tumor cells, which are then gradually reabsorbed and expelled by the body over 3-18 months.
How long does the procedure take?
The procedure is performed in our office and takes less than 30 minutes. Most patients report minimal discomfort and are able to resume normal activity right away. Since no breast tissue is removed, the shape of the breast is maintained and little, if any, visible scarring occurs.
Who is a good candidate for cryoablation?
Cryoablation is a safe and effective option for patients whose breast tumor is less than 4 cm in diameter, visible on sonogram and has been confirmed with a biopsy.
Pictured below you will find a step-by-step example of the process of Cryoablation along with an animation of the procedure